Table of Contents
The Impact of Social Media on High-Risk Youth Mental Health

Written By: Elizabeth Kroll

Clinically Reviewed By: Clary Figueroa
December 24, 2024
5 min.
Findings about the negative effects of social media on youth mental health are particularly concerning for vulnerable populations, like those with serious conditions.
Learn more about our Clinical Review Process
Table of Contents
Since the introduction of social media in the mid to late 2000s, adolescent usage has increased exponentially. According to a study done by the Pew Research Center in 2023, at least one in five adolescents report being on social media “almost constantly.” However, in recent years, this so-called addiction to social media has raised concerns for parents, teachers, and child psychologists alike.
Many worry about the impact constant connectivity has on sleep, self-esteem, and the ability to form in-person connections. These concerns are particularly acute for vulnerable populations, including young people dealing with high-risk mental health conditions — like those at Charlie Health. Read on to learn more about what we’ve found about how social media affects these clients.

Support for young people struggling with their mental health
Virtual, intensive treatment with other people who get it.
The current state of adolescent mental health and social media
The current state of adolescent social media usage is in a time of flux. As data continues to come out about teen social media usage and the effect that it has on adolescents, law and policy changes are likely to follow. Some are already beginning to take shape, signaling that the social media landscape for teens may look very different in the years ahead.
Australia recently banned all social media usage for anyone under the age of 16. Instagram has implemented a new type of account for users between the ages of 13-17, which limits the content they’re able to see, limits who can contact them, sends in-app reminders to take breaks from social media, and automatically mutes all notifications overnight. Even parents and schools are working together on the Phone-Free Schools Movement, which is supported by Dr. Jonathan Haidt, one of the leading researchers in the field.
These reactions are not unfounded. In May 2024, the U.S. Surgeon General released an advisory regarding social media usage and youth mental health, indicating that increased social media usage may change brain development in adolescents, potentially impacting impulse control and risk-taking behaviors. Research done by Dr. Twenge and Dr. Haidt has shown that there is a significant association between social media usage and poor mental health in teenage girls. Furthermore, research has indicated that there are specific windows of development in which increased social media usage leads to a decrease in overall life satisfaction.
However, there are conflicting views on the correlation versus causation of this data. For instance, Dr. Candice Odgers argues that while we do see increased mental health symptoms in adolescents who use social media more, a likely explanation is that adolescents with mental health issues gravitate towards social media. In other words, mental health symptoms predate social media usage, not the other way around. Despite these differing perspectives, one thing remains clear: the conversation around adolescent social media usage and mental health is far from over, and understanding this relationship is crucial for guiding future policies and practices.

Charlie health data: How social media affects high-risk youth
This ongoing debate about social media and its impact on teens shows just how complicated the issue is. While studies and policies highlight real concerns, there’s still a lot we don’t know about whether social media causes mental health struggles or if it’s the other way around. That’s why we’ve been following the latest research and even collecting our own data to better understand how social media fits into the bigger picture of teen mental health.
At intake, Charlie Health clients spend an average of 12-15 hours on social media per day, with the majority of those hours being spent on TikTok (2.0 – 3.5 hours), YouTube (3 – 4 hours), or Instagram (~2 hours). In comparison, screen time for other reasons, such as TV or work, falls somewhere between 1-5 hours per day.
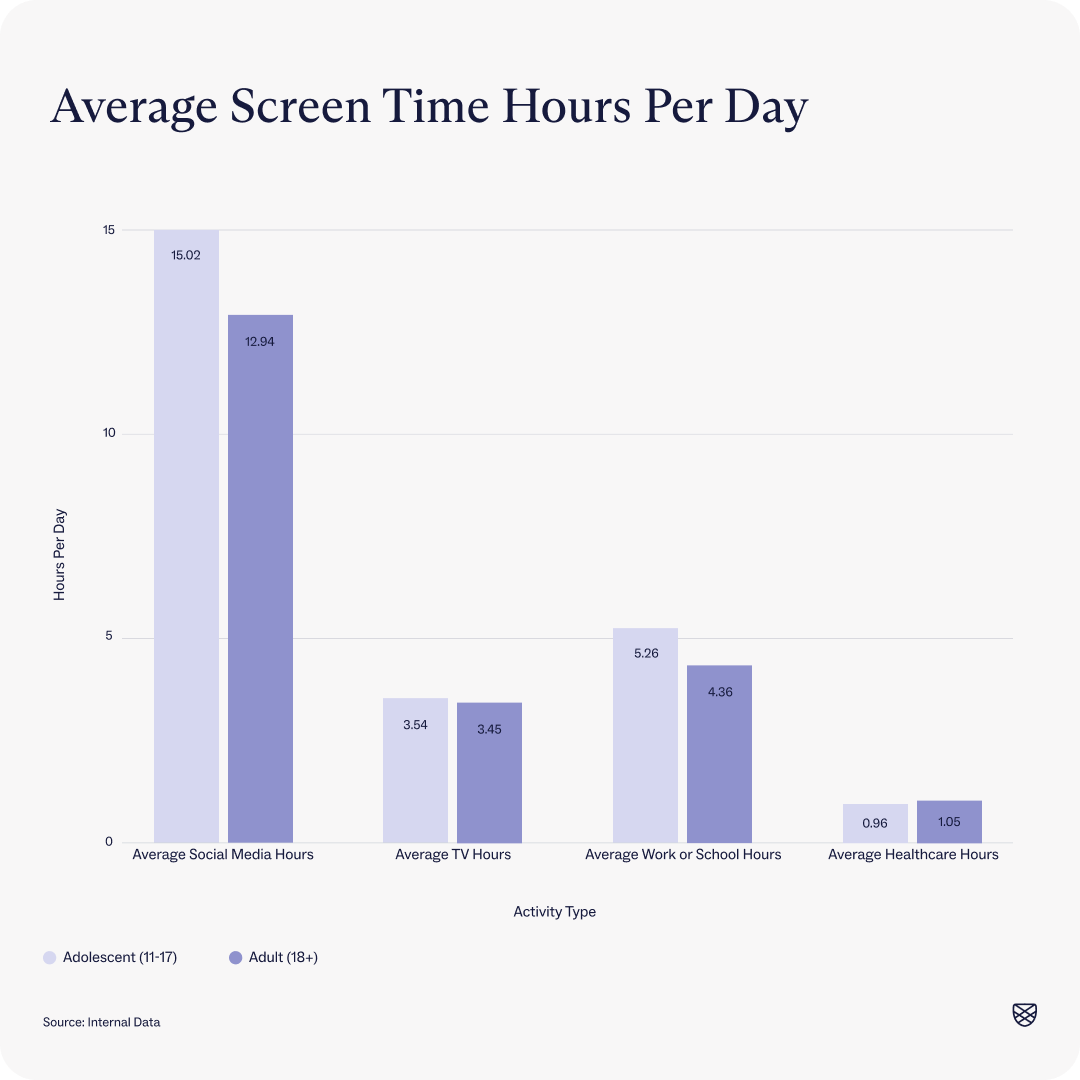
Adolescent sample size = 3469 / Adult sample size: 5323
Unlike previous literature, average depression and anxiety scores at intake did not differ significantly depending on how much time a client spent on social media. This may be due to the fact that all Charlie Health clients start at a high baseline for mental health symptoms, so social media usage may not have as strong a relationship with mental health at this level of acuity.
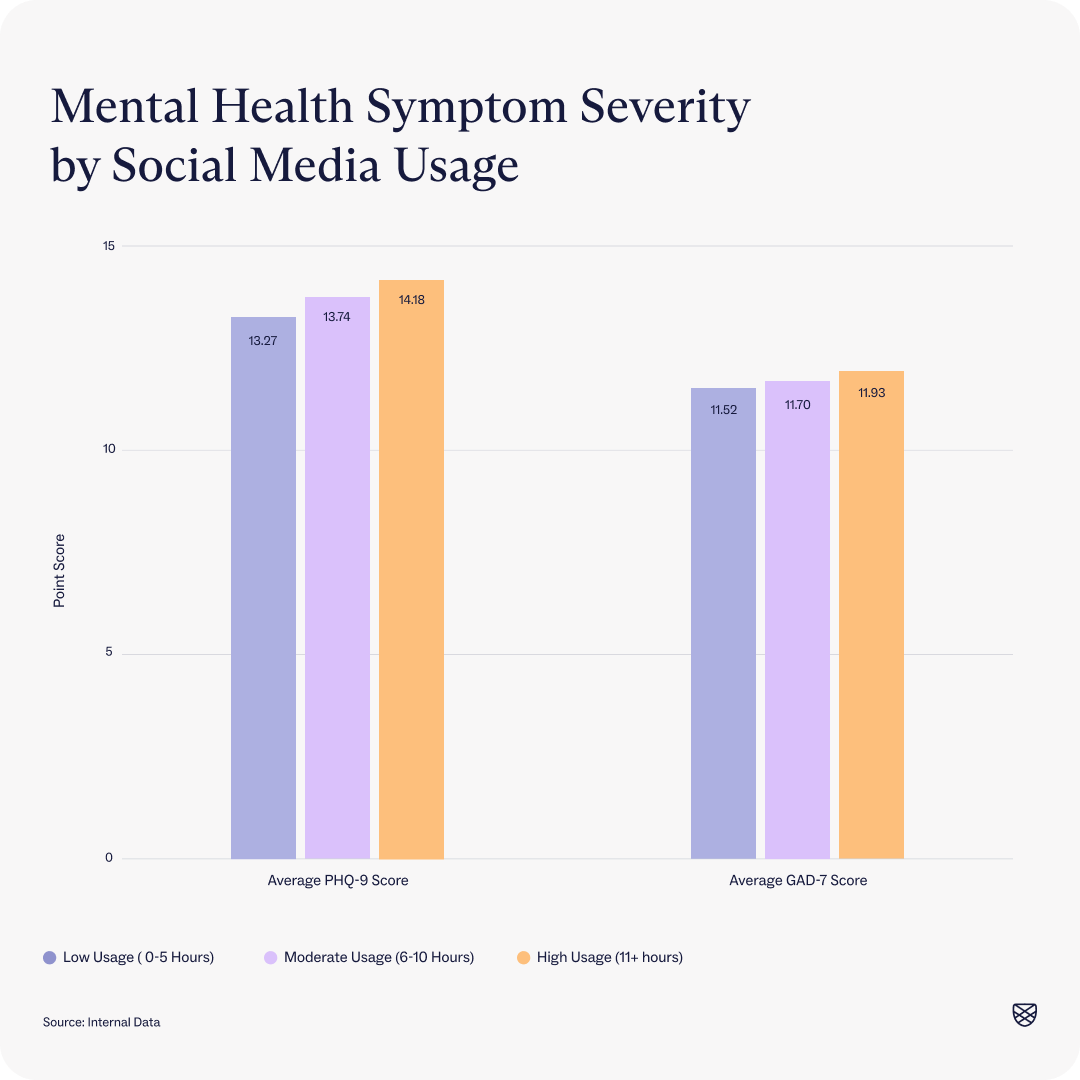
Low Usage Sample Size = 2726 / Moderate Usage Sample Size = 2525/ High Usage Sample Size = 3541
However, clients at intake do report that the harder they find it to limit their social media usage, the higher their depression and anxiety symptoms are. This finding may indicate that while the actual number of hours someone spends on social media may not play a significant role in their symptoms, their feelings of self-control are associated with their depression and anxiety symptoms.
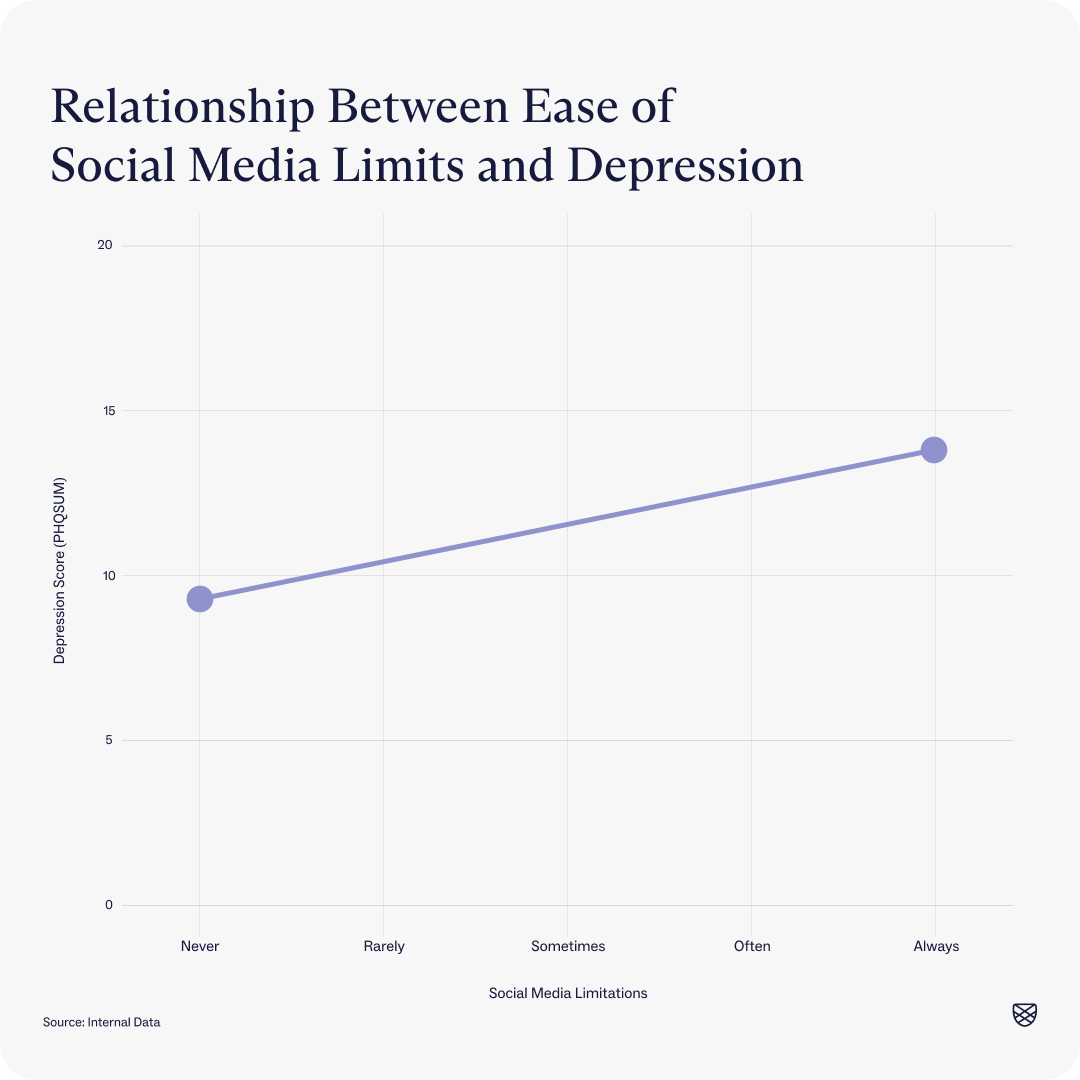
t(7987) = 20.93, p<.001, sample size: 7989
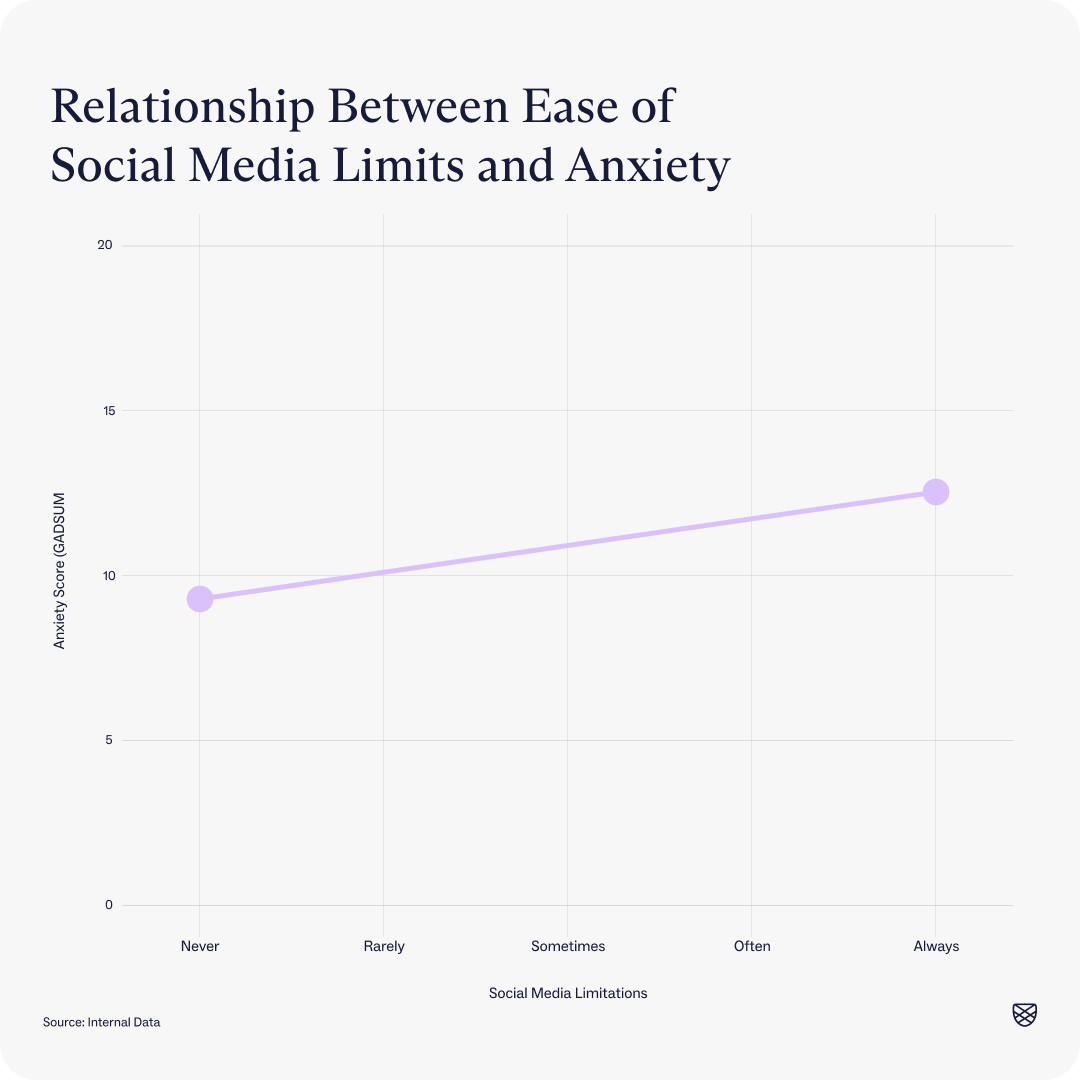
t(7846) = 16.63, p<.001, sample size = 7848
As these questions were added to our data collection process somewhat recently, we do not yet have a large enough sample from clients at discharge to make any significant claims. Keep an eye out later in the year for an update on this data!
Our findings: Social media and serious mental health issues
The intersection of adolescent social media usage and mental health is a complex and evolving topic. While some studies highlight potential risks, such as changes in brain development and heightened mental health symptoms, others suggest that social media may not be the root cause of these challenges but rather a reflection of pre-existing issues. At Charlie Health, our data underscores this complexity: while the amount of time spent on social media doesn’t always correlate with mental health symptoms, feelings of control—or lack thereof—over social media usage seem to play a significant role.
As we continue to explore these questions, one thing is clear: addressing adolescent mental health in the age of social media requires a nuanced and data-driven approach. It’s not just about limiting screen time but understanding how teens interact with these platforms and how those interactions influence their well-being. At Charlie Health, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of this research to better support our clients and their families.
How Charlie Health can help
If social media is affecting your or a loved one’s mental health, Charlie Health is here to help. Charlie Health’s virtual Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP) provides more than once-weekly mental health treatment for people dealing with serious mental health conditions, including the mental health effects of social media. Our expert clinicians incorporate evidence-based therapies into individual counseling, family therapy, and group sessions. With this kind of holistic online therapy, managing your mental health is possible. Fill out the form below or give us a call to start your healing journey today.
References
https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2023/12/11/teens-social-media-and-technology-2023/
https://www.npr.org/2024/12/19/nx-s1-5231020/australia-top-regulator-kids-social-media-ban
https://about.instagram.com/blog/announcements/instagram-teen-accounts
https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/sg-youth-mental-health-social-media-advisory.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0001691822000270
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29296-3
https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=NY6k-twAAAAJ&citation_for_view=NY6k-twAAAAJ:t6usbXjVLHcC




